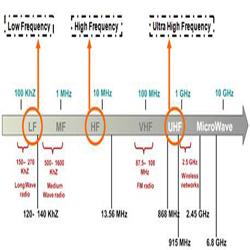
RFID frequency range
posted on: 24 May, 2018 | 04:17:28 PM by ibc
1.Low Frequency RFID
The LF band covers frequencies from 30 KHz to 300 KHz. Regularly LF RFID systems work at 125 KHz, in spite of the fact that there are some that work at 134 KHz. This recurrence band gives a short read scope of 10 cm, and has slower perused speed than the higher frequencies, yet is not exceptionally delicate to radio wave impedance.
LF RFID applications incorporate access control and domesticated animals following.
Gauges for LF creature following systems are characterized in ISO 14223, and ISO/IEC 18000-2. The LF range is not viewed as a really worldwide application on account of slight contrasts in recurrence and power levels all through the world. Low-frequency tags have a long wave-length and are better able to penetrate thin metallic substances. Additionally, LF RFID systems are ideal for reading objects with high-water content, such as fruit or beverages, but the read range is limited to centimeters or inches. Typical LF RFID applications include access control and animal tagging.
2.High-frequency RFID
High Frequency (13.56 MHz) Used where medium data rate and read ranges up to about 1.5 meters are acceptable. High-frequency tags work fairly well on objects made of metal and can work around goods with medium to high water content. Typically, HF RFID systems work in ranges of inches, Typical HF RFID applications include tracking library books, patient flow tracking, and transit tickets.
3.UHF frequency OF RFID
Ultra High-Frequency (850 MHz to 950 MHz) typically offer much better read range (inches to 50+ ft. depending on the RFID system setup) and can transfer data faster (i.e. read many more tags per second) than low- and high-frequencies. However, because UHF radio waves have a shorter wavelength, their signal is more likely to be attenuated (or weakened) and they cannot pass through metal or water. Due to their high data transfer rate, UHF RFID tags are well suited for many items at once, such as boxes of goods as they pass through a dock door into a warehouse or racers as they cross a finish line. Also, due to the longer read range, other common UHF RFID applications include electronic toll collection and parking access control.
- Applications for RFID within the supply chain can be found at multiple frequencies and different RFID solutions may be required to meet the varying needs of the marketplace. Since UHF (Ultra High Frequency) has the range to cover portals and dock-doors it is gaining industry support as the choice frequency for inventory tracking applications including pallets and cases.
RFID tags are further broken down into two categories:-
- (a) Active RFID Tags are battery powered. They broadcast a signal to the reader and can transmit over the greatest distances (100+ meters). They can be used to track high value goods like vehicles and large containers of goods. Shipboard containers are a good example of an active RFID tag application.
- (b) Passive RFID Tags do not contain a battery. Instead, they draw their power from the radio wave transmitted by the reader. The reader transmits a low power radio signal through its antenna to the tag, which in turn receives it through its own antenna to power the integrated circuit (chip). The tag will briefly converse with the reader for verification and the exchange of data. As a result, passive tags can transmit information over shorter distances (typically 3 meters or less) than active tags. They have a smaller memory capacity and are considerably lower in cost making them and ideal for tracking lower cost items.
There are two basic types of chips available on RFID tags, Read-Only and Read-Write:-
- Read only chips are programmed with unique information stored on them during the manufacturing process – often referred to as a „number plate? application. The information on read-only chips can not be changed.
- Read-Write chips the user can add information to the tag or write over existing information when the tag is within range of the reader. Read-Write chips are more expensive than Read Only chips. Applications for these may include field service maintenance or „item attendant data? – where a maintenance record associated with a mechanical component is stored and 5 updated on a tag attached to the component. Another method used is called a "WORM" chip (Write Once Read Many). It can be written once and then becomes "Read only" afterwards.
http://www.indianbarcodecorporation.com/knowledge-base
MINDWARE
S -4, Plot No-7, Pocket-7, Pankaj Plaza,
Near Metro Station, Sector-12,
Dwarka, New Delhi-110078, (India)
+91-11-46102688 DIRECT LINE
Mobile:+91-9810822688, +91-9717122688